Wake Up 101
The Science of Waking Up
Did you know our sleep center is actually connected to our eyes, not our ears? That’s why the harsh noise of an alarm clock is so harmful – it goes against our natural biology in every way. Get ready for Dr. Kathy’s crash course in Waking Up 101!
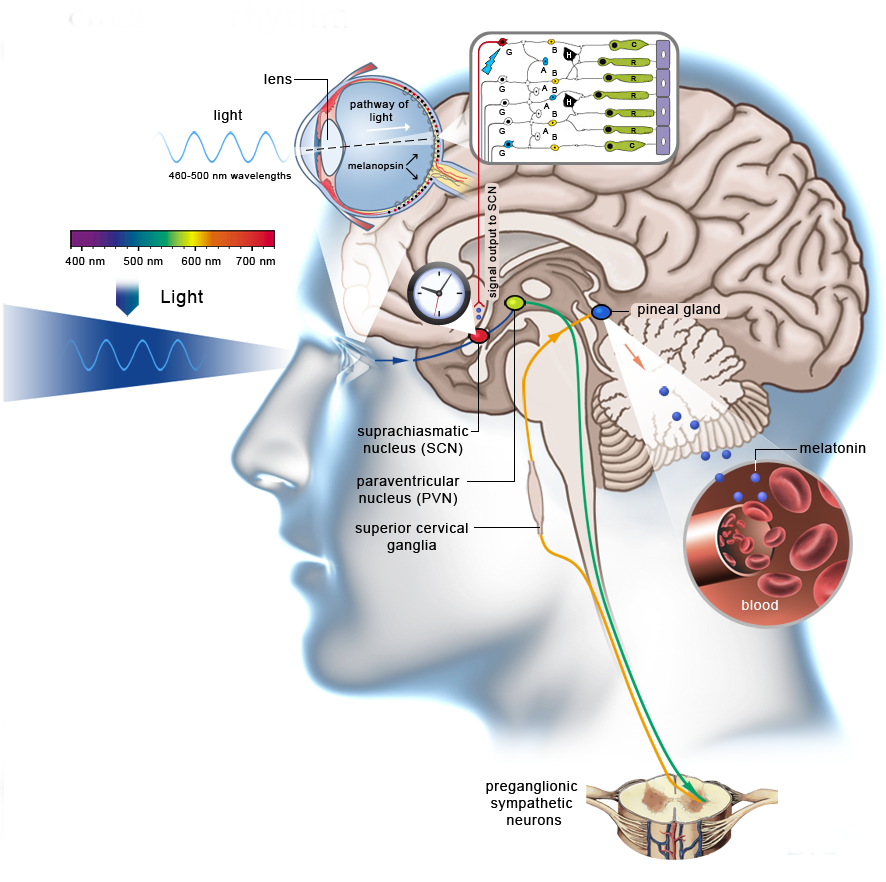
Meet the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
Our eyes have a specific way of responding to light, even when they are closed. It all starts with the suprachiasmatic nucleus. It is located in the hypothalamus part of our brain, a region that helps regulate our circadian rhythms. Our eyes contain light-specific nerve tracks that send signals from photoreceptor cells called melanopsin. These relay information about light waves directly to the suprachiasmatic nucleus. It’s pretty cool that our eyes are designed to detect light in addition to visual input!

Understanding Melatonin
The suprachiasmatic nucleus is considered to be our sleep center. When it senses light, it tells the pineal gland to suppress melatonin. Decreasing melatonin is what triggers us to switch from sleeping to wakefulness. This is when we experience wakeup cues such as an elevated heart rate, a rise in body temperature, and increased cortisol levels. This process results in our “rise and shine” response every day.

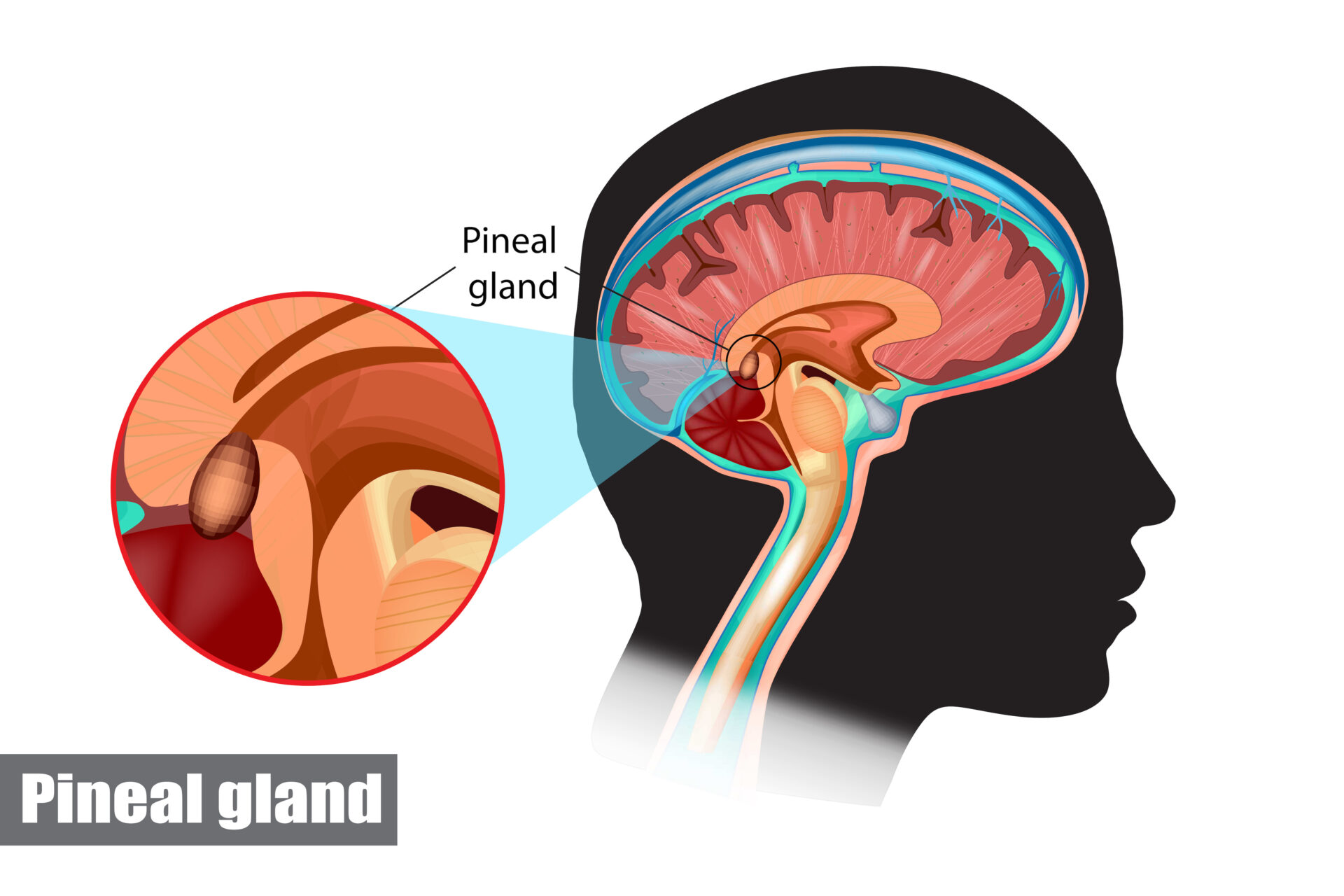
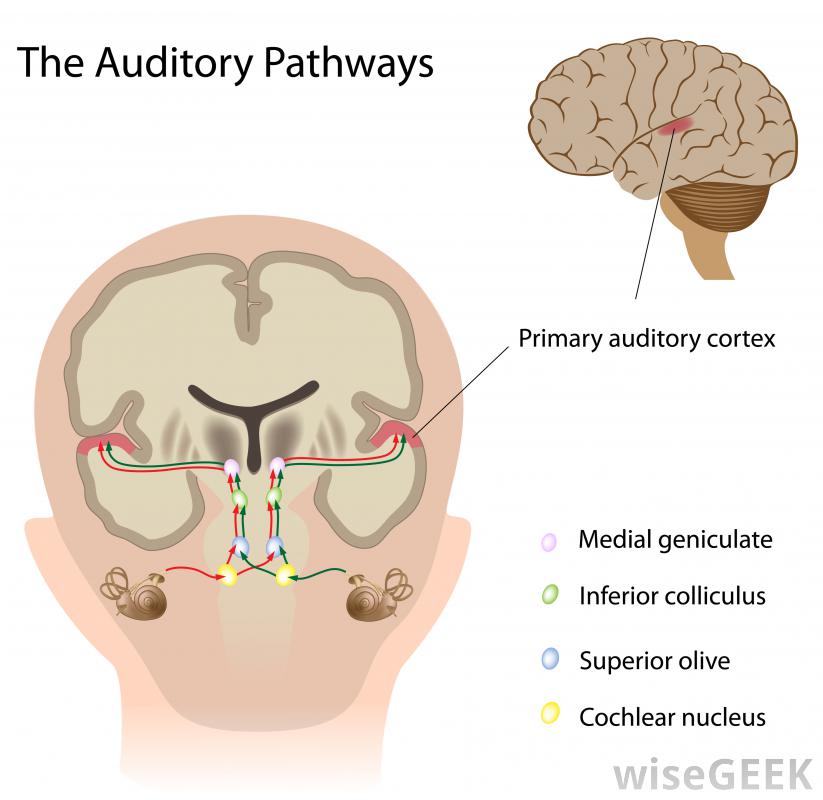
The Sound of Silence
Have you guessed what’s not present in our sleep-wake cycle? Sound! The auditory cortex – the area of the brain that processes sound – is completely separate. It’s even located in the temporal lobe, a different part of the brain than the hypothalamus. Our temporal lobe is focused on processing auditory stimuli as well as encoding memories.

Know Your Anatomy!
Circadian Rhythm
Biological patterns over a 24-hour cycle.
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus
The internal clock that governs our circadian rhythm; located in the hypothalamus.
Hypothalamus
The part of the brain that links the endocrine and nervous system; one of its main functions is to regulate sleep.
Melanopsin
Photopigments created in our retinal cells that travel to the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
Melatonin
A hormone related to our sleep cycle that is made by the pineal gland, which is connected to the hypothalamus.
Temporal Lobe
The part of the brain that oversees speech, hearing, and memory.

Light Awake – The Calming Wakeup Experience
 Light Awake uses pulsating light to gently rouse you from sleep. There are no sharp, piercing noises that startle you awake. Its flashing light is designed to stimulate your circadian system and comfortably move your mind from slumber to consciousness. This is the only wakeup system that is based on the physiology of our eyes and brain.
Light Awake uses pulsating light to gently rouse you from sleep. There are no sharp, piercing noises that startle you awake. Its flashing light is designed to stimulate your circadian system and comfortably move your mind from slumber to consciousness. This is the only wakeup system that is based on the physiology of our eyes and brain.
Free App Download
Light Awake’s silent alarm clock is a natural way to rouse from your sleep. There are no sharp or piercing noises that startle you awake. Its gentle light stimulates your circadian system so you comfortably move from slumber to consciousness.
